|
Background The design of the study is described in Case Study 3 and further details of the experimental design are given in Baker et al. (1999) and Baker et al. (2003) . Throughout six years from 1991 to 1996 Dorper (D), Red Maasai (R) and Red Maasai - Dorper crossed ewes were mated to Red Maasai and Dorper rams to produce a number of different lamb genotypes. For the purposes of this example, only the following four offspring genotypes are considered: D x D, D x R, R x D and R x R. 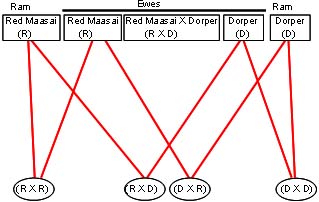
|
Case Study 3 explores the nature of associations between various factors such as age of dam and sex of offspring on weaning weight in a fixed effect least squares analysis of variance. As well as comparing the performance of the different genotypes when exposed to helminthiasis, it is also of interest to examine genetic variation among rams and ewes within genotypes. To do this we need to use what are known as ´restricted ´ or ´residual maximum likelihood ´ (REML) procedures which are able to simultaneously estimate random and fixed effects. Once the random estimates are known these can then be used to obtain heritability estimates which determine the proportion of the variation among offspring that has been handed down from parents. |