Disciplined Use of Spreadsheets for Data Entry
Date of publication: January 2001
This is one of a series of guides for research and support staff involved in natural resources projects. The subject-matter here is the disciplined use of spreadsheets for data entry. Other guides give information on allied topics. Your comments on any aspect of the guides would be welcomed.
- Introduction
- An example
- Facilitating the data entry process
- The metadata
- Checking the data after entry
- More complicated data sets
- Conclusions
We have used Excel 97, which is part of the Microsoft™ Office 97 suite of programs. Excel and Office are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. All other product or brand names mentioned herein may be trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies and are hereby acknowledged.
1. Introduction
In our guide on Data Management Guidelines for Experimental Projects we noted that spreadsheets are commonly used for data entry because they are familiar, in widespread use and very flexible. However, we also stated, as a warning:
Their very flexibility means they can result in poor data entry and management. They should thus be used with great care. Users should apply the same rigour and discipline that is obligatory with more structured data entry software.
This guide is to explain what we mean by "great care" and "rigour and discipline" and hence to show how a spreadsheet package can be used effectively for data entry. In the illustrations we have used Excel as an example of a spreadsheet package, but the principles apply equally to other spreadsheets.
Our example datasets are taken from experimental studies, but the ideas are also applicable to surveys and participatory studies. An example of a survey dataset in Excel is used in the guide entitled The Role of a Database Package in Managing Research Data.
We begin the next section with a simple example that shows some data that have been poorly entered: we discuss the problems that can then arise. In Section 3 we consider features in Excel that facilitate simple and reliable data entry. The rationale here is that the simpler the data-entry process, the more reliable will be the data that are entered.
In Section 4 we describe how to organise the data-entry process. This emphasises the value of setting up the worksheet to include all the metadata, i.e. all associated background information relating to the data. The metadata includes where the data came from, when they were collected, what the data values represent and so on.
Simplifying the data-entry process and recognising the importance of the metadata has implications for the task of organising the data-entry system within a spreadsheet. It is important to separate this task of preparing the spreadsheet for data entry from the actual entry of the data. The preparatory phase now takes a little longer, but our assertion is that the extra effort is justified.
Finally we cover some other issues, including validation checks after data entry, and the entry of more complicated data sets.
2. An example
Figure 1 shows a typical data set that has been entered in Excel. This is a simple set of data that can be entered very effectively in a spreadsheet.
Figure 1. A typical data set in spreadsheet style
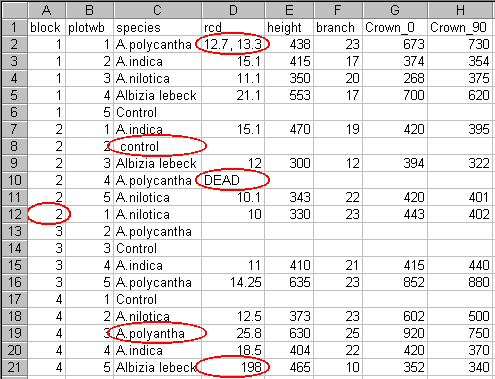
The data were entered by a clerk, who - as instructed - typed what was written on the recording sheet in the field. However, this has led to errors (ringed in Figure 1). For example, two of the names under the "species" heading have been typed slightly differently from the names for the same species used elsewhere in the same column. In the column headed "rcd", row 2 has two measurements entered, while in row 10, instead of a numerical value, the cell reports that the plant is dead. Such entries will cause problems when the data are transferred to a statistics package for analysis.
Most of these errors can be avoided if some thought is given to the layout of the data in the spreadsheet before data collection in the field commences. This activity is in fact the responsibility of the researcher, not of the data-entry clerk. This guide attempts to show how to avoid these problems.
There are other deficiencies if these data are all that is to be computerised. For instance, there is no indication as to where the data came from, when the data were collected or what they represent. There is no record of the units of measurements used. Such information is highly relevant and should be included with the data in the spreadsheet. This is especially true if the dataset is to be integrated with datasets from other studies, or is to be passed to someone else for analysis. The entry of the metadata is discussed in Section 4.
You may think that this example is a caricature and that real data would not be entered so poorly. Figure 2 shows some of the data from Figure 1 entered in a different way.
Figure 2. An alternative way to enter data
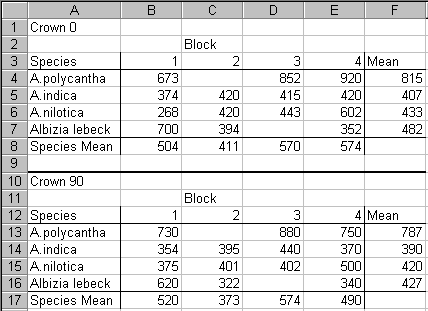
The layout in this example is even worse. It confuses data entry and analysis.
The display of the data, shown in Figure 2 is sometimes convenient as a prelude to the analysis. We sehow, in Section 5, that it is easy with Excel to enter the data properly and then display the values as shown in Figure 2.
You should not necessarily expect the software to help in recommending good procedures for data entry. For example, if you decided to use Excel for the analysis of variance, then it would expect the data in the form shown in Figure 2.
You would then find that Excel's facilities for ANOVA are limited (see the guide Excel for Statistics: Tips and Warnings). The next step might be to ask about transferring the data to a statistics package but you would not find a good statistics package that accepts the data in the tabulated form shown in Figure 2. They all expect it in the "rectangular" shape shown in Figure 1.
Thus, as we stated at the beginning of Section 1, Excel gives you total flexibility to enter your data as you wish, but no guide as to how to enter the data well.
3. Facilitating the data-entry process
3.1 Introduction
3.2 Freezing or splitting panes
3.3 Drop-down lists
3.4 Data validation
3.5 Adding comments to cells
3.6 Formatting columns
3.7 Data auditing
3.1 Introduction
This section describes how the data could have been entered so as to eliminate the mistakes and discrepancies illustrated in Figure 1. If the guidelines, given in the following sections, had been applied, the data could look like Figure 3.
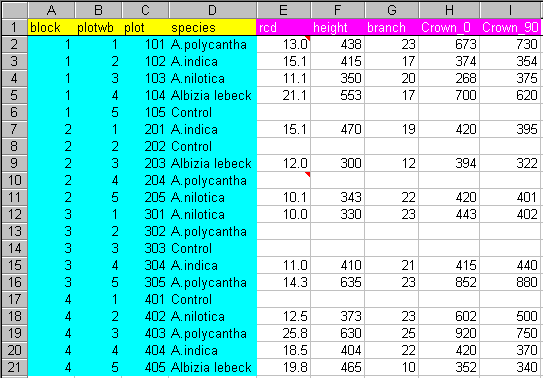
It is sensible to spend a little time thinking about the data before rushing into using Excel. In this example, the entries in the columns A to D were determined at the planning stage of the experiment and are the same for all the measured variables. They could have been entered into the spreadsheet before any measurements were taken. A paper printout of Figure 4, which includes additional metadata information (see Section 4), could then have been used in the field to collect the data.
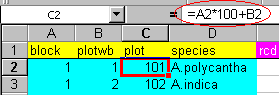
If you compare Figure 1 with Figure 3, you will notice that there is an extra column, named plot. It is useful to have a column that uniquely defines each row of data. In this example, after the block and plotwb (plot within block) columns have been entered, plot has been calculated as follows: plot=100*block+plotwb (the formula is shown ringed in Figure 5).
When the data have been collected, you may decide to format the columns so that the data are displayed, for example, to two decimal places for heights or lengths, or as integers for data in the form of counts. You may wish to have range checks, so that typing data outside the minimum and maximum values is prohibited. You can add comments to cells to indicate, for example, that an animal has died or that a tree has been destroyed by an elephant!
The next few sub-sections illustrate some of these ideas.
3.2 Freezing or splitting panes
When entering data, it is useful to be able to keep the headings of columns always visible as you scroll down the screen. This can be achieved by freezing the panes. For example, if in Figure 3, the row below the headings, i.e. row 2, is highlighted, then by selecting Window > Freeze Panes, the headings in row 1 will always be displayed, regardless of how many rows of observations are entered. The same effect can be achieved by choosing Window > Split. To remove the freezing or the split, select Window > Unfreeze Panes or Window > Remove Split.
3.3 Drop-down lists
There are usually ways to avoid typing a sequence more than once. If the species column had a repeating list of text strings, these could be typed just once and then the spreadsheet's Fill option from the Edit menu could be used to fill the remaining cells.
In Figure 1, the species names do not follow a repeating pattern. This is a common situation in a field experiment, where the treatments (here, of species) are allocated at random (i.e. by means of a deliberate process of randomisation). The four species plus the control are each repeated four times within the column. When the same text string is entered many times, typing errors inevitably occur. In the example in Figure 1, the species name "A.polycantha" has been mis-typed as "A.polyantha" in block 4.
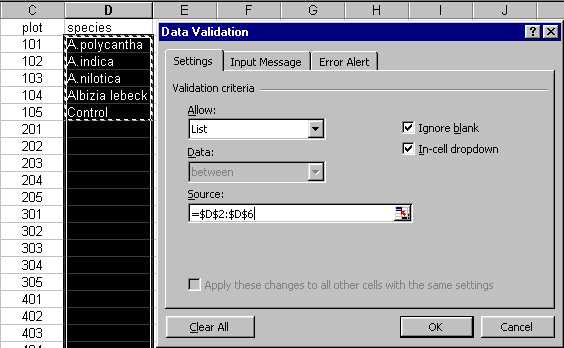
Figure 6 shows the creation of a drop-down list. The five species names for block 1 are entered into cells D2:D6. These five names can then be used to create the drop-down list. Highlight all the species data cells, i.e. D2:D21 as in Figure6. Select Data > Validation > Allow: > List. For the Source of the list, highlight the names already typed for block 1, i.e. cells D2:D6 (as shown).
Once the drop-down list has been created, selecting a cell in that column will bring up an indicator triangle on the right side of the cell. Clicking on this will display the drop-down list (see Figure 7). An appropriate selection can then be made from the drop-down list.
New data entered in these cells must either be a string from the given list, or else the cell can be left blank. Entry into the cells can be forced by unchecking the Ignore blank field in the Data Validation dialog box shown in Figure 6.
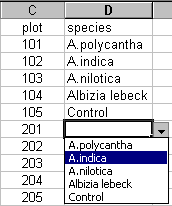
The rest of the species can now be selected from the drop-down list. For example, Figure 7 shows the selection of A.indica for plot 201.
Using drop-down lists for data entry helps to ensure that errors in spelling do not occur.
3.4 Data validation
Validation checks can and should be set on ranges of cells within the spreadsheet. A range could be an entire column/row, several columns/rows, or just a single cell. The validation rules apply when new data are entered.
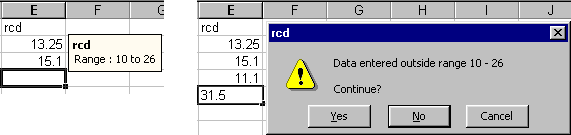
One validation tool available in Excel is the facility to set up range checks for numerical data. For example, the measurements recorded for the variable rcd are expected to be in the range from 10 to 26. To set up a range check, highlight cells E2 to E21, select Data > Validation > Allow: > Decimal and set the Minimum as 10 and the Maximum as 26 as shown in Figure 8. At the same time, an Input Message and an Error Alert can be set up and their effects are shown in Figure 9. The Input Message is displayed when each cell in the column is activated (Figure 9a). This reminds the data-entry person of the range of values allowed. The Error Alert Message is displayed when a value outside this range is typed (Figure 9b). Note that only the data cells are highlighted, not the variable name at the top.
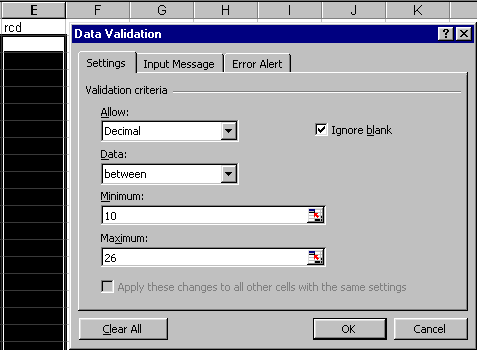
Figure 9a Figure 9b
3.5 Adding comments to cells
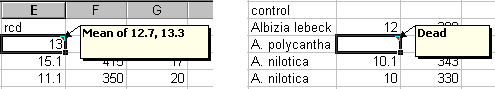
Excel has a facility for adding comments to a cell. These differ from values within the cell. Comments should be used for any unusual observations or questions concerning a particular data value. When entering the data for rcd, a decision had to made for plot 101, where two values were entered on the data recording sheet. We chose to calculate the mean and add a comment to the cell, as shown in Figure 10.
If there had been several plots with two values recorded, two columns of rcd data could have been entered and a third column could have been used to calculate the mean. With the specific cell highlighted, the menu sequence Insert > Comment allows comments to be entered.
Comments are also useful in explaining why certain values are missing. For example, in Figure 1 the value DEAD had been entered in cell D10. This string is inappropriate for the cell but can be put as a comment to indicate why the value is missing. Figure 10 shows comments that have been added to cells. A comment is set on a single cell but can be copied to a range of other cells.
When you wish to remove a comment from a cell, for example when a query has been resolved and the correct value has been entered, highlight the cell, select Edit > Clear > Comments.
3.6 Formatting columns
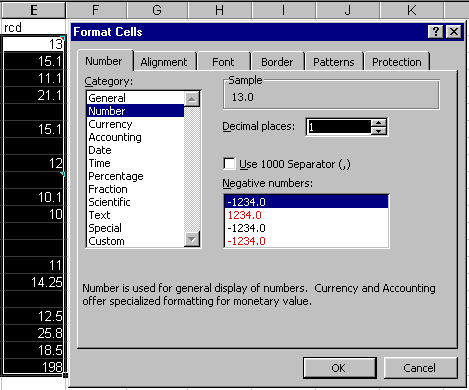
Excel suppresses trailing zeros by default. For example, in Figure 10 the value 13.0 is displayed as 13. To display the column of data to 1 decimal place, highlight the data, then use Format > Cells > Number > Decimal places > 1 as shown in Figure 11. This also shows that there is flexibility in how the data are displayed, e.g. font size, cell borders.
3.7 Data auditing
The suggestions given above are all intended to aid data entry. However, there is also a facility, known as auditing, using Tools > Auditing..., for checking data that have already been entered. It is recommended that you use this facility whenever you add validation rules following the data entry or when you make changes to existing rules. Validation rules are very flexible. The type of data such as whole number, decimal, text, etc., can be specified; data not of the correct type will be rejected on data entry. You can then set further restrictions to accept only those numbers within a given range, or text strings of a particular length, for example.
We illustrate auditing, on the data in Figure 1, where validation rules have been added for both species and rcd. Select Tools > Auditing... and click on Show Auditing Toolbar. >From this toolbar (Figure 12), click on the icon, second from right, Circle Invalid Data. Figure 12 shows the errors circled in red for the variables rcd and species.
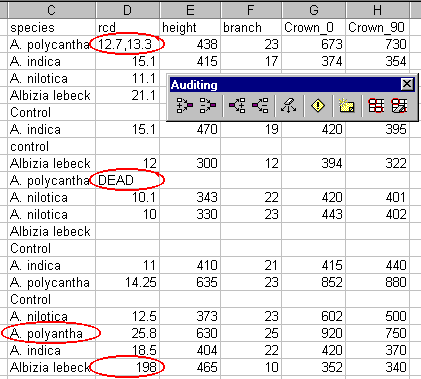
With the exception of the column header, all cells in a column should have the same data type. In the case of column D, the data type is numeric. The string "DEAD" in cell D10 is therefore inappropriate.
4. The metadata
4.1 Overview
4.2 Body data
4.3 Column information
4.4 Page information
4.5 Entering the date
4.6 Using multiple sheets
4.1 Overview
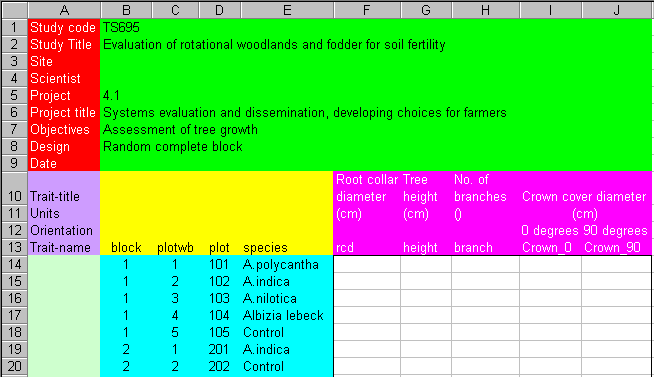
In the previous section we looked at some methods of validating data both during data entry and afterwards. However the data we started with is still not complete. In this section we advocate adding rows and columns to the spreadsheet before the body of data. These extra rows will store documentation that provides background information about the data, i.e. it comprises the "metadata".
Figure 13 shows a blank spreadsheet divided into input areas. The sizes of these areas are not fixed but can grow or shrink depending on the data to be entered.
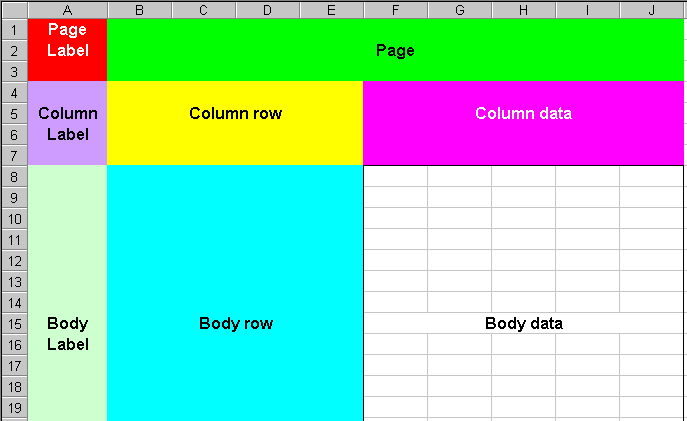
Figure 14 shows the data from Figure 3 with this structure.
It is useful to adhere to a strict code as to what should be entered into each section of the spreadsheet. Keep in mind the following three aims:
- Encourage completeness;
- Avoid unnecessary duplication;
- Minimise errors.
4.2 Body data
The Body data area contains all values that have been observed or measured. With reference to the data in Figure 3, this is the range of cells E2:I21. It is the range F14:J33 in Figure 14. Values in columns A to D (of Figure 3) are not measurement data but correspond to information relating to the design of the experiment. These, with the exception of the first row, fall into the Body row area of Figure 13. The Body Label area can be used to add more information about the body data.
4.3 Column information
In the column label, column row and column data areas we add information to describe the measurements. Here a measurement corresponds to a unique identifiable column of data.
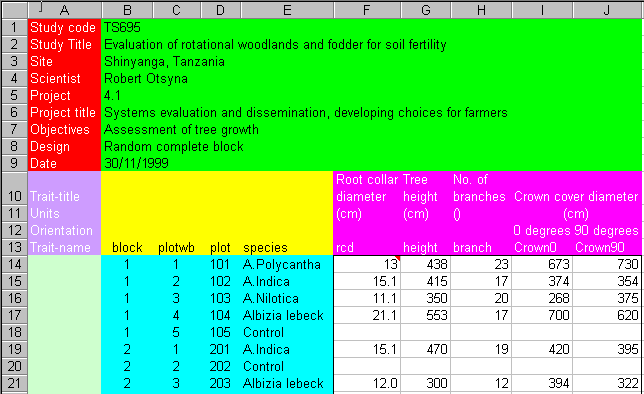
The column headers in the first row of Figure 3 go into the column data areas of Figure 13. We still need more information. For instance, the data file does not clarify what specific measurements are being made, so it is necessary to include a description of what rcd, height, branch, etc. actually represent. It is also necessary to specify the units of measurement being used for each of these variates. These are shown in Figure 14.
4.4 Page information
All that remains to be entered now is documentation related to the whole dataset. Effective documentation requires that, given a data set, one should be able to retrieve the original protocol plus all other related data. This documentation appears in the Page area of the spreadsheet with the Page Label area providing labels for each piece of information. The minimum documentation is the study code and its title. It is also useful to include the location where the data was collected and the name of the person responsible for the study. The study objectives, the design and other protocol details should be entered if available.
4.5 Entering the date
All observed raw data should be associated with a date of observation. Before entering the date of measurement ensure that the computer date setting matches the expected date input format. Remember that 9/2/99 could refer either to 9 February 1999 or 2 September 1999 depending on the date settings on your computer. (These can be checked by selecting Settings > Control Panel > Regional Settings from the Windows Start menu.) To ensure you have the correct date, use Format > Cell > Date and choose a display setting that includes the name of the month, e.g. 9 February 1999.
If all observations are taken on the same date, the date should be entered in the Page section with an appropriate label in the Page label area. This is shown in Figure 14. If this is not the case the dates should be entered into the Body row area with an appropriate label in the Column row. Where there are a limited number of dates, for example where the values were measured on one of just three or four dates, a drop-down list should be created with these dates and values chosen from the list on data entry.
4.6 Using multiple sheets
Entering the data plus the metadata as described above gives us Figure 14.
An alternative is to put the "Page information" on to a separate sheet in the Excel Workbook. This is often convenient when there is a lot of information at the dataset level.
In such cases you may still have a small "Page" section in each data sheet that describes the type of measurements that are entered in that sheet.
5. Checking the data after entry
5.1 Use of plots to highlight outliers
5.2 Data/Filter as a data checking tool
5.3 Tabulations
We have demonstrated in Section 3 how auditing can be done to check existing data against the validation rules. This is a single operation using the menu sequence Tools > Auditing... requesting the auditing tool bar and selecting the option circle invalid data. Here we give some further steps that may be undertaken to validate the data after it has been entered.
5.1 Use of plots to highlight outliers
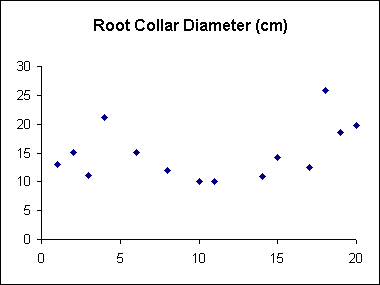
Scatter plots are useful tools for helping to spot suspicious inputs (i.e. outliers). Many would be trapped at the data-entry stage if validation rules had been set up but there may still be some values that differ substantially from the rest. Figure 15 shows a scatter plot of Root Collar Diameter where the x-axis corresponds to the order in which the values appear in the data file. This plot shows that all data records lie from about 10 units to about 25 units.
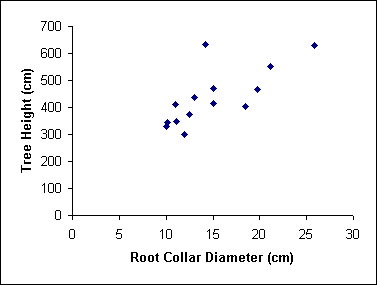
Such a plot is quick and easy to produce and can be done for all observed variables. It is also useful to produce scatter plots of pairs of variables if knowledge about the two variables being plotted are expected to show a definitive pattern. Figure 16 shows tree height plotted against root collar diameter. There is at least one suspicious observation.
5.2 Data/Filter as a data checking tool
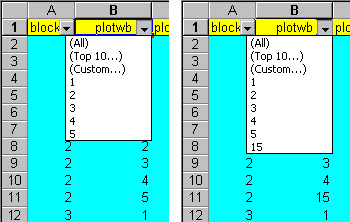
In the example dataset we are using, we know that there are four blocks with five plots in each block. In Figure 17a, the Data > Filter > AutoFilter option has been used for plotwb. Clicking the autofilter tab for plotwb gives a list of values in that column. It shows that only values 1 to 5 have been entered in plotwb. If, for example, the value 15 had been entered instead of 5, the list would also contain the value 15 (Figure 17b) and so the error could be spotted.
5.3 Tabulations
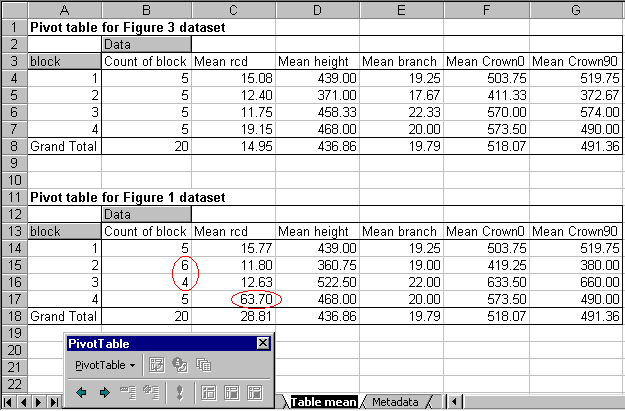
Frequency tables can be generated using Excel's pivot table facility. Generating tables in Excel is described in Appendix 1 of the guide Excel for Statistics: Tips and Warnings.
In Figure 18, the count of the number of observations within each of the 4 blocks plus the means of the variables are shown for the data in Figure 3 and Figure 1. Using pivot tables is another way of spotting data-entry errors.
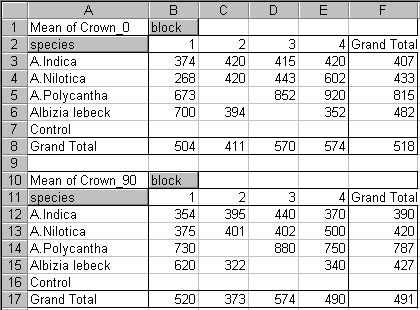
Note that, if you had required your data to be in the layout shown in Figure 2, this could have been accomplished using pivot tables, as shown in Figure 19.
6. More complicated data sets
There are various ways that studies can produce data that have a more complicated structure than the example considered here. The most common complication is when measurements are taken at different levels. For example, a survey might have data at the "village", "household" and "person" level. For illustration, we consider an example of an experiment with some data at the "plot" level and other measurements at the "plant" level.
To emphasise the concepts, we illustrate the system in Excel by means of a set of figures, with minimal explanation. Readers wanting more details could look at the notes from the Data-entry Course Notes that were prepared by the Statistical Services Centre for the Institut de Recherche Agronomique de Guinée (IRAG). The notes are available from the SSC web site.
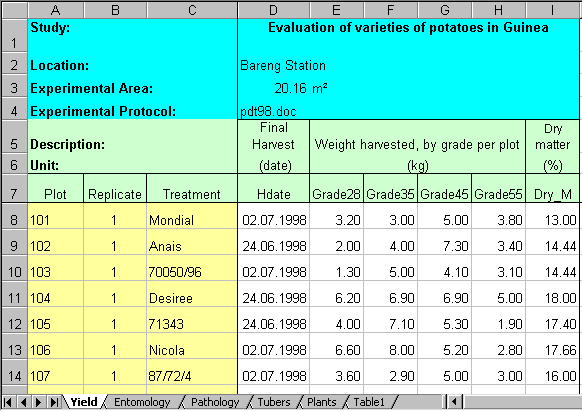
The data are taken from an experiment to compare nine different varieties of potatoes. The design is a randomised complete block with 3 replicates, giving 27 plots in all. Within each plot, some measurements were made at the plot level while others were made on 20 plants within each plot.
The Excel workbook used for the data entry comprises six worksheets, as shown in Figure 20.
The Yield worksheet holds the metadata and some of the measurements made at the "plot" level. The Entomology and Pathology worksheets also contain data for the 27 plots.
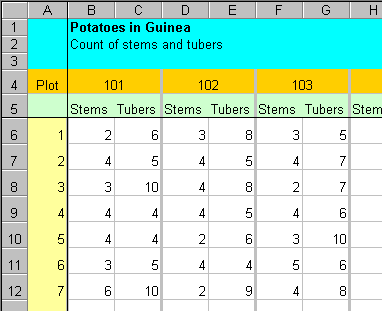
Figure 21 shows the design of the Tuber worksheet that was used for entering the "plant" level data, and was a "copy" of the paper data collection sheet. The body of the sheet contains 20 rows (plants) and 27 (plots) * 2 (counts of the number of stems and tubers) columns. This layout makes it easier for the data collection person to record the counts. Figure 22 shows part of the worksheet with some data entered.
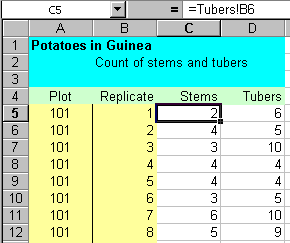
The Plants worksheet is a copy of the data in the Tuber worksheet, with the data reorganised into columns of length 540 (i.e. 27 plots * 20 plants). It is shown in Figure 23, where, for example, cell C5 = cell B6 in the Tuber worksheet. Data cannot be entered into the Plants worksheet, but it is automatically updated, whenever a change is made to the Tuber worksheet. This arrangement of the data is the format needed to generate pivot tables. An example is shown in Figure 24. Again, changes in the original data are updated in this table.
Be aware that if there is a blank in the cell Tubers!B6, then the cell C5 will contain a zero. The way round this is to use an "if" function, for example, "=IF(Tubers!B6="","",Tubers!B6)".
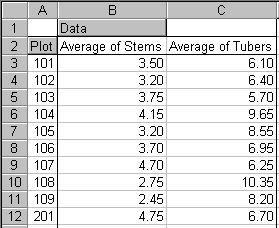
The final worksheet, Table 1, was generated using the pivot tables facility in Excel. It gives the plot means for each of the 20 plants within a plot.
7. Conclusions
Our main conclusion is that a spreadsheet package, such as Excel, can be used for effective data entry, particularly for data sets with a simple structure.
Even for simple data entry, it is important to separate the task of organising the spreadsheet from that of actually entering the data.
Excel provides a range of aids to effective data entry, some of which have been described in Section 3 of this guide.
It is simple and useful to include the "metadata" within the data-entry process. Compare Figure 14 with Figure 1 to review the potential of Excel for complete data entry for simple data sets.
It is also possible to use Excel for the entry of more complex data sets, as was outlined in Section 6 of this guide. This takes more planning and we recommend that, for such tasks, consideration also be given to the use of a database package, such as Access, or a specialised data-entry system, such as EpiInfo, which is distributed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Atlanta, U.S.A. More information about EpiInfo can be found from the Internet at http://www.cdc.gov/epiinfo/ (from where the package can be downloaded free of charge).
In supporting the use of a spreadsheet package for data entry we have been driven, to some extent, by its popular use. It is clear that many people will continue to use a spreadsheet for their data entry and this document suggests ways of making the entry effective. There are limitations. For example there are no easy facilities for skipping fields conditional on the entry of initial codes. There are no automatic facilities for "double entry". The graphics in Excel that were illustrated in Section 5, are meant primarily for presentation; there are no boxplots (or other exploratory techniques) that could assist in data scrutiny.
Spreadsheets are intended as "jack-of-all-trades" software. They are certainly not the master of data entry. Hence if the data-entry component is large, or complex, we suggest that a spreadsheet should not be the only contender for the work.
Last updated 23/04/03